Electronic Leak Detection (ELD) Explained
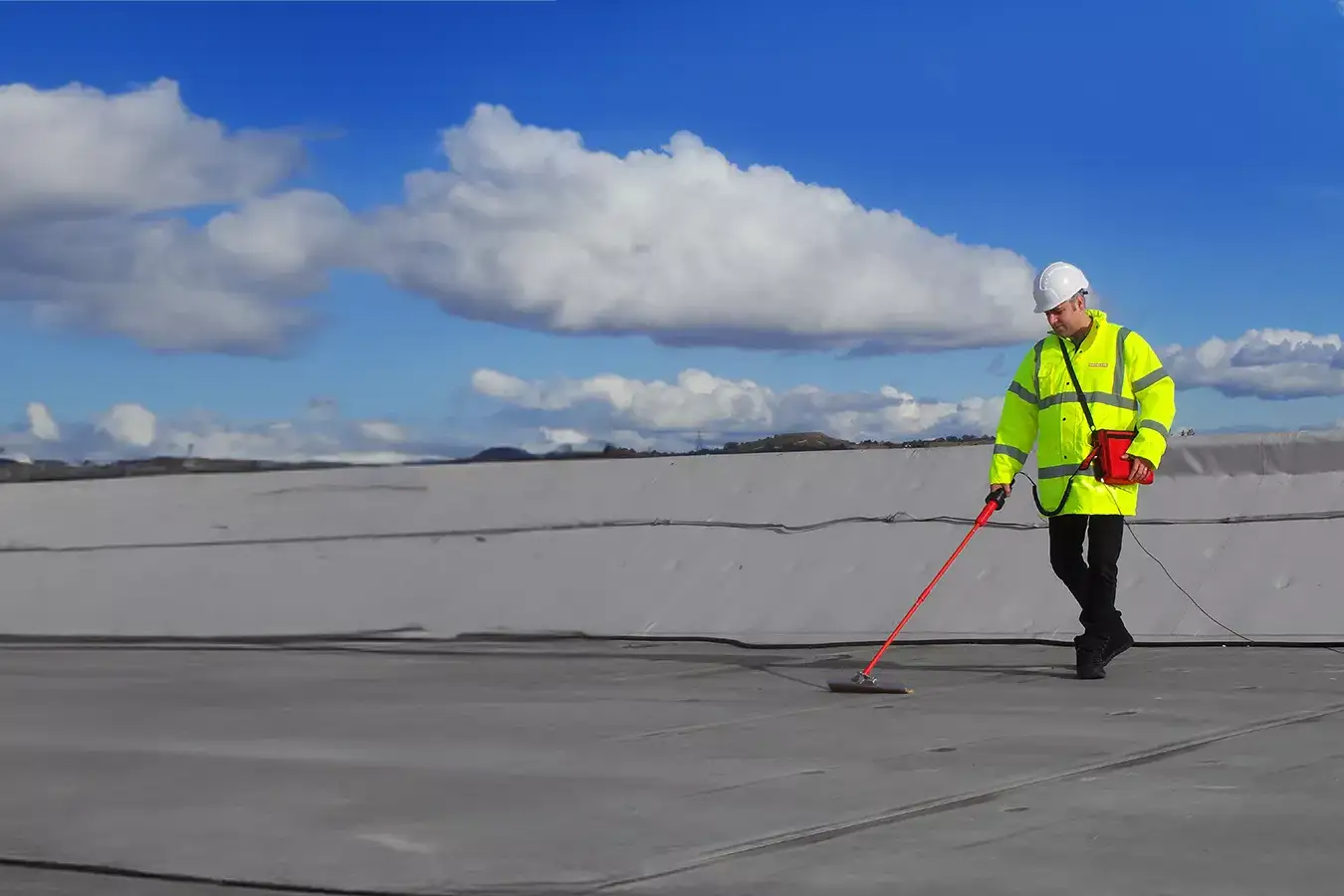
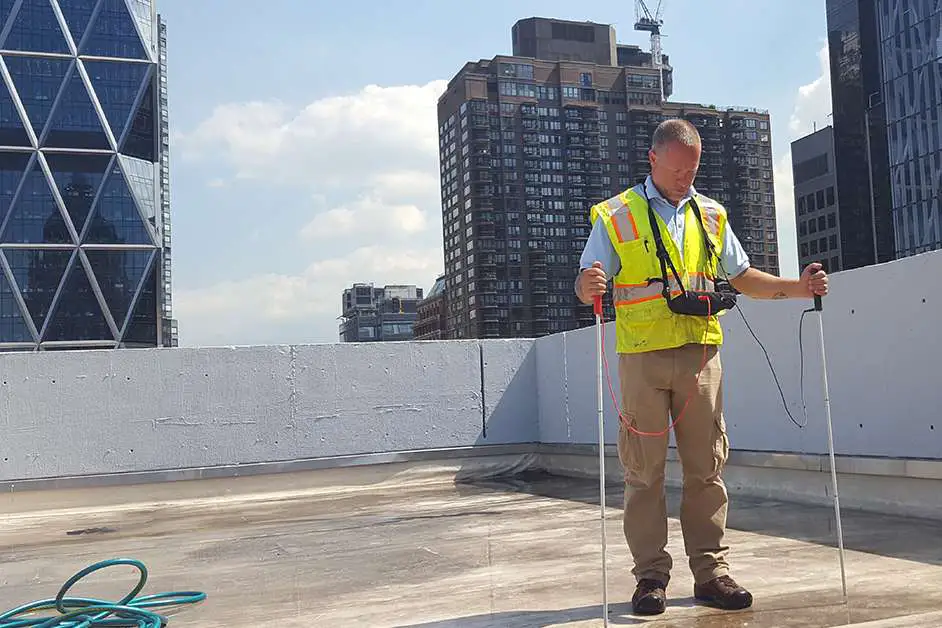
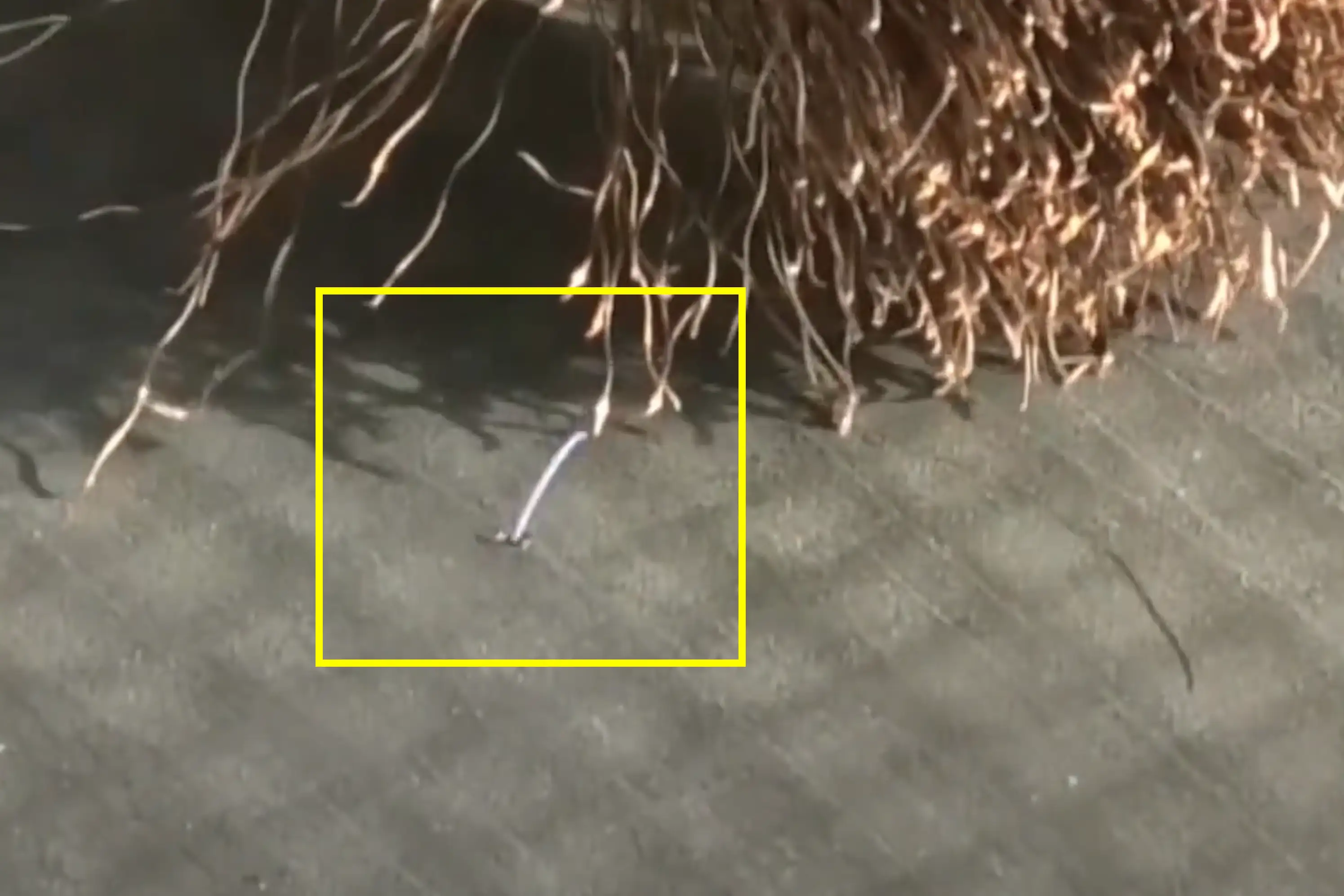
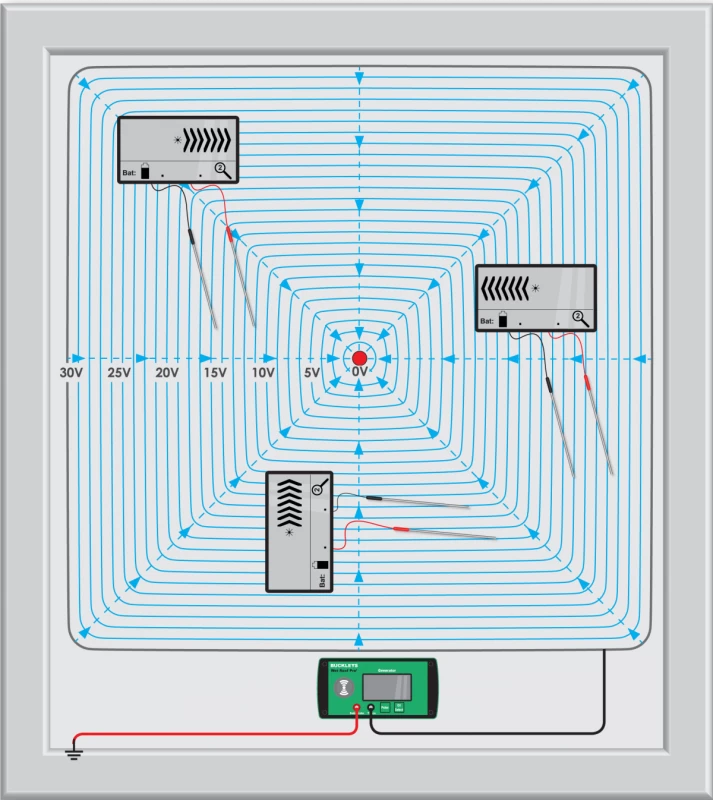
Electronic leak detection is a technique used to identify leaks in roofing membranes and other waterproofing systems. It utilizes electrical currents or electromagnetic fields to pinpoint the exact location of a leak. This method is particularly effective for flat roofs, where traditional visual inspections might miss subtle or hidden damage. A prerequisite is however that the substructure is conductive and earthed through foil isolation layers, steel decking or concrete which are earthed. This technique is best suited to large commercial buildings rather than residential. There are two common types of electronic roof leak detection, wet testing or dry testing.